

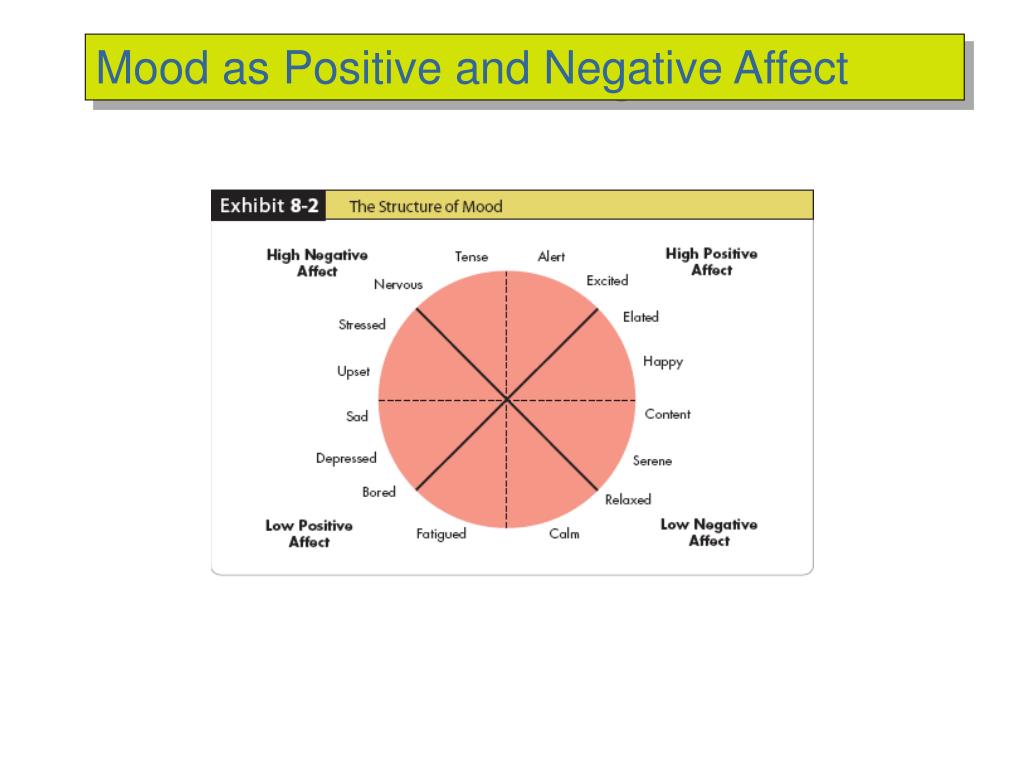
In the workplace, these events may include not having your opinions heard, a lack of control over your day-to-day environment, and unpleasant interactions with colleagues, customers, and superiors. Negative emotions such as anger, fear, and sadness can result from undesired events. This is because being positive can lead to upward positive spirals where your good mood brings about positive outcomes, thereby reinforcing the good mood (Frederickson & Joiner, 2002). Positive feelings have been shown to dispose a person to optimism, and a positive emotional state can make difficult challenges feel more achievable (Kirby, 2001). As a result, it may cause you to feel fulfilled and satisfied. A positive feeling generates a sensation of having something you didn’t have before. Individuals experiencing a positive emotion may feel peaceful, content, and calm. In the workplace, these events may include achieving a goal or receiving praise from a superior. Positive emotions such as joy, love, and surprise result from our reaction to desired events. Emotions can influence whether a person is receptive to advice, whether they quit a job, and how they perform individually or on a team (Cole, Walter, & Bruch, 2008 George & Jones, 1996 Gino & Schweitzer, 2008). For example, a manager’s way of speaking can cause one person to feel motivated, another to feel angry, and a third to feel sad. Not everyone reacts to the same situation in the same way. More formally, an emotion is defined as a short, intense feeling resulting from some event. The root of the word emotion comes from a French term meaning “to stir up.” And that’s a great place to begin our investigation of emotions at work. For employees, however, the value of a job is also emotional. 2017 83:135-141.doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2017.06.Financial analysts measure the value of a company in terms of profits and stock. Cortisol stress response in post-traumatic stress disorder, panic disorder, and major depressive disorder patients. Wichmann S, Kirschbaum C, Böhme C, Petrowski K.
Examples of negative moods how to#
Minimum time dose in nature to positively impact the mental health of college-aged students, and how to measure it: a scoping review. Meredith GR, Rakow DA, Eldermire ERB, Madsen CG, Shelley SP, Sachs NA. Evidence of the importance of dietary habits regarding depressive symptoms and depression.

Acute bouts of exercising improved mood, rumination and social interaction in inpatients with mental disorders. Depression and risk of stroke: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. The effect of contact with natural environments on positive and negative affect: A meta-analysis. Your face and moves seem happier when I smile: Facial action influences the perception of emotional faces and biological motion stimuli. Marmolejo-Ramos F, Murata A, Sasaki K, et al. Relationship between sleep quality and mood: Ecological momentary assessment study. Triantafillou S, Saeb S, Lattie EG, Mohr DC, Kording KP. Factors contributing to depressive mood states in everyday life: A systematic review. Why not everyone gets their fair share of stress: adolescents’ perceived relationship affection mediates associations between temperament and subsequent stressful social events. Laceulle OM, Jeronimus BF, van Aken MAG, Ormel J. people with cyclothymic disorder may have relatively brief periods of normal mood in between episodes. Cyclothymia: This disorder is characterized by milder forms of alternating mania and depression.Symptoms of SAD may include fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and social withdrawal. This disorder is characterized by depressive symptoms that generally occur during the winter months, when there is less natural sunlight. Seasonal affective disorder (SAD): Formerly known as major depressive disorder with seasonal pattern.
People with bipolar disorder may also have manic episodes, during which they may act impulsively, have racing thoughts, and be easily irritated. Bipolar disorder: This disorder is characterized by extreme changes in mood, from mania (a high, often euphoric state) to depression.People with depression may also have trouble sleeping, eating, and concentrating. Major depressive disorder: This serious condition can cause a person to feel persistently sad, anxious, or empty.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
